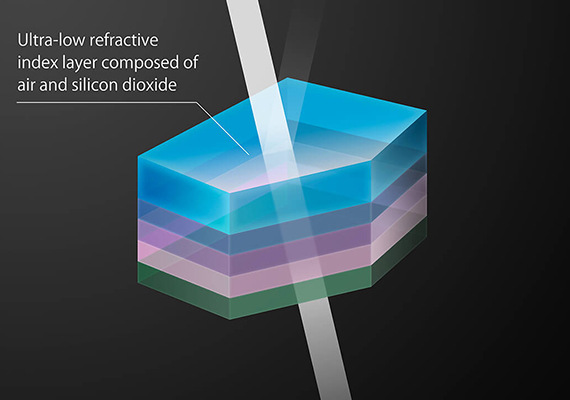
BR Lens
BR Lens
New optical element developed for ideal correction of chromatic aberration
White light is a mixture of various successive wavelengths of light (red, green, blue, etc.). Because the refractive index varies according to the wavelength, lenses made with regular glass are not able to focus all the wavelengths on a single point on the image plane and the shifted wavelengths appear as color fringing in resulting images. This color fringing – called chromatic aberration – has long been the Achilles heel of lens performance. As part of ongoing efforts to correct chromatic aberration, Canon successively developed and implemented fluorite, UD, and Super UD lenses. Now, aiming to achieve ideal correction of chromatic aberration, Canon has developed BR (Blue Spectrum Refractive) optics, delivering anomalous dispersion characteristics equal to or surpassing fluorite.
BR optics is based on a new organic optical material, developed by reexamining lens material from its molecular structure. This new lens material features unique anomalous dispersion characteristics that are capable of greatly refracting blue light (short wavelengths spectrum), which has traditionally been difficult to focus on a single point. Incorporation of a BR lens, consisting of BR optics sandwiched between concave and convex glass lenses, makes it possible to control the path of blue light (short wavelength spectrum), producing clear, sharp images by thoroughly reducing chromatic aberration. This makes it possible to achieve excellent rendering performance from large-aperture lenses, traditionally susceptible to chromatic aberration, even when shooting at maximum aperture. BR optics offer new potential for high performance lens design.

Cause of Chromatic Aberration
White light is composed of a mixture of light of various wavelengths (red, green, blue, etc.). Since the refractive index varies according to wavelength, it is not possible to get all wavelengths of light to focus on a single point on the image plane by normal glass material. This appears as color fringing in images, and is called chromatic aberration.

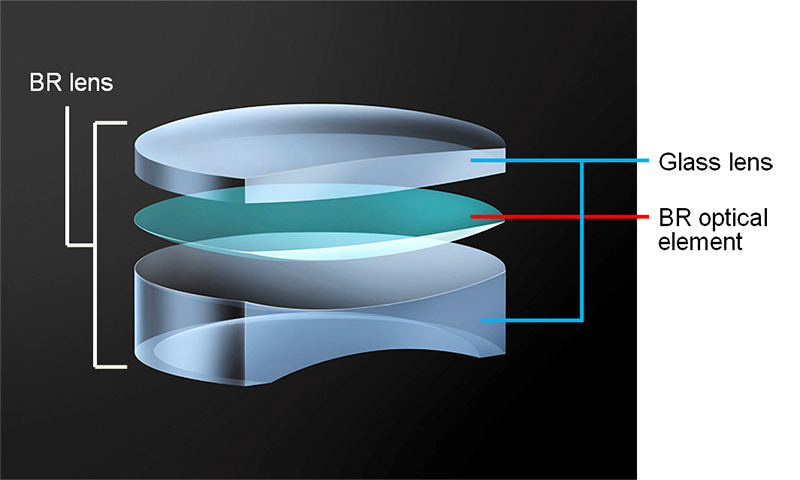
Blue Spectrum Refractive Optics (BR Optics)
By reviewing lens materials from its molecular design, Canon succeeded in developing a unique lens material using organic optical material as its raw material – the Blue Spectrum Refractive Optics (BR Optics). BR optics is characterized by its ability to greatly refract blue light (short wavelength spectrum), a wavelength that, until now, had proven particularly difficult to converge to a specific focal point.
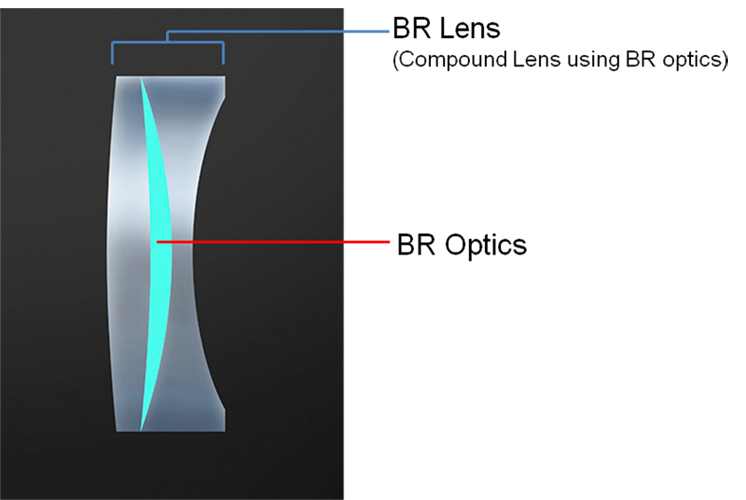
To utilize BR optics as camera lens element, a BR Lens is formed by sandwiching the BR optics between a convex and concave glass lens element. As a result, a greater standard of correction has become possible and superior imaging performance has been achieved even for lenses that were impossible to correct for chromatic aberration using conventional technology.
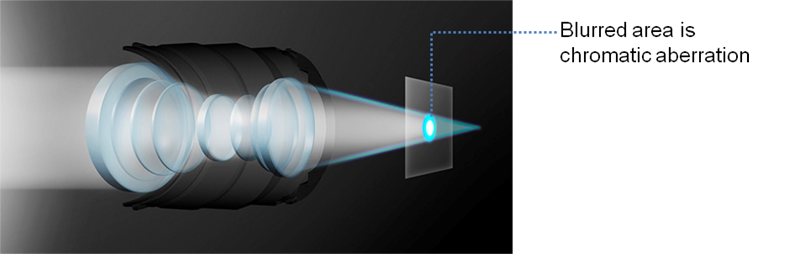
Normal Glas
Merely combining convex and concave lenses will not correct blue wavelengths refraction and the shifted focal point will appear as blue color fringing.
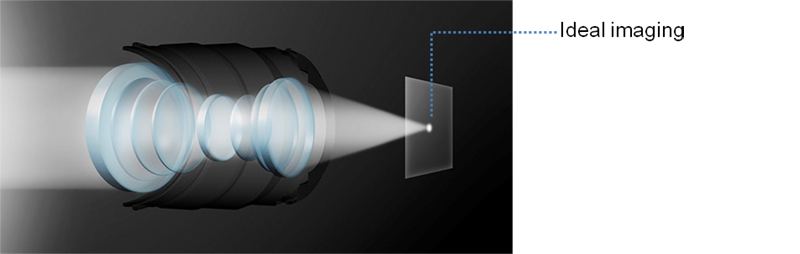
BR Lens
Since a BR lens can greatly refract blue light (short wavelength spectrum), placing it between a concave and convex lens allows all visible light wavelengths to be focused onto a single point.
Application of BR Lens
Comparison 1: Highly Reflective object
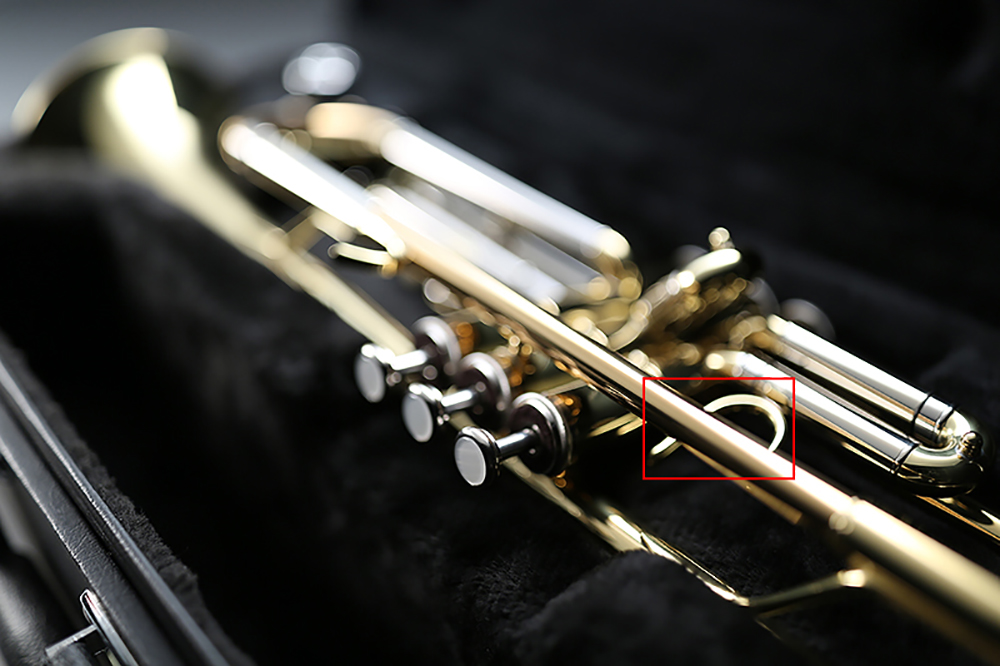

EF 35mm f/1.4L USM
EF 35mm f/1.4L II USM
Axial chromatic aberration is significantly reduced
Comparison 2: Glassware
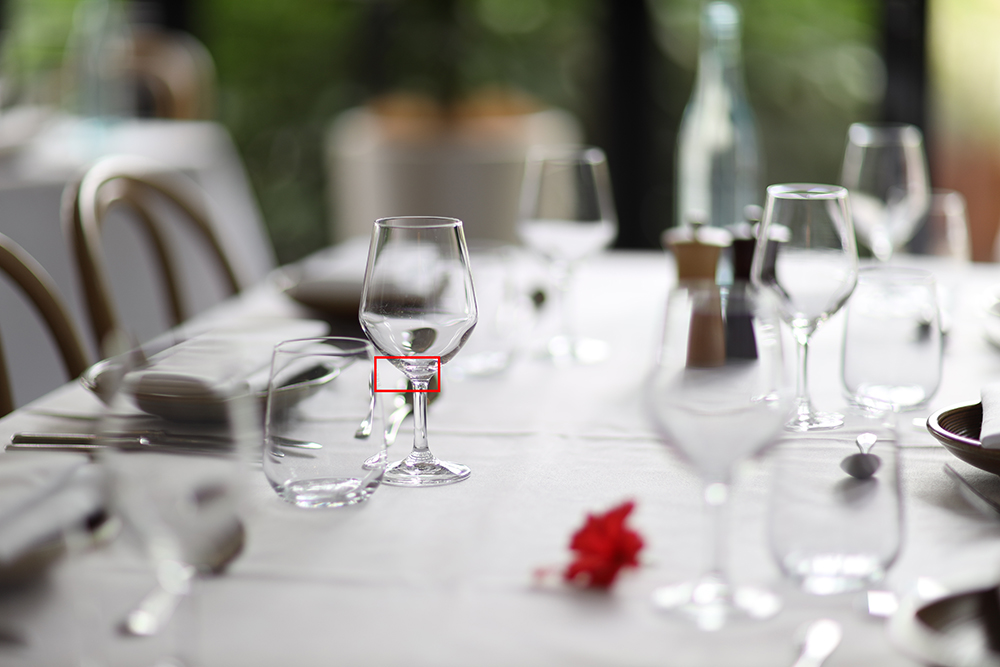

EF 85mm f/1.2L II USM
RF 85mm f/1.2L USM
Chromatic aberration is greatly reduced
Comparison 3: Landscape
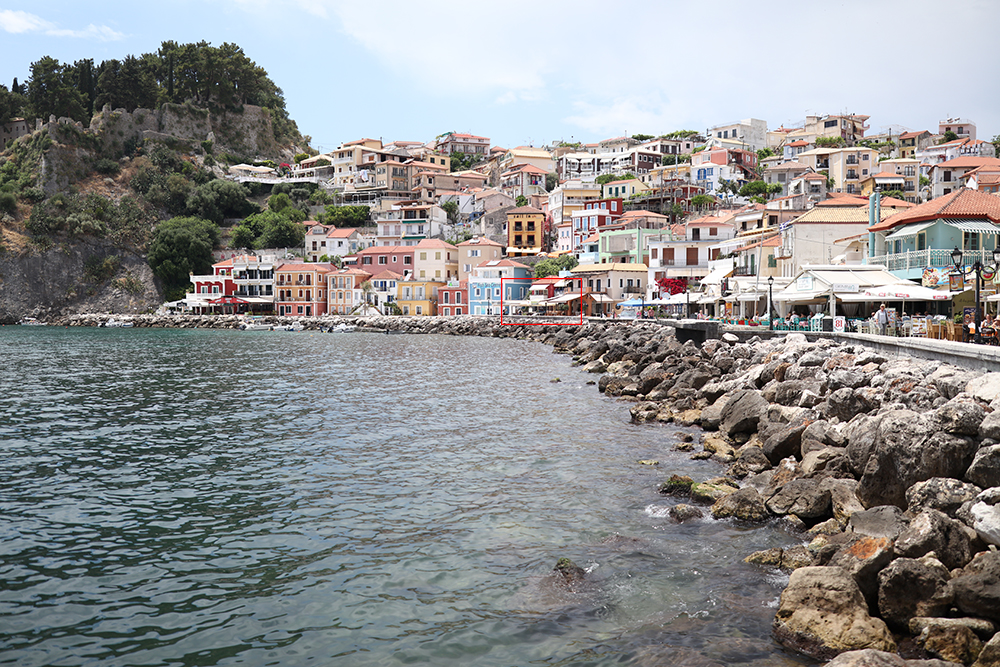

EF 35mm f/1.4L USM
EF 35mm f/1.4L II USM
Magenta color fringing is significantly reduced